Acne breakouts can occur anywhere on the skin, with common areas being the face, neck, shoulders, back, and chest. The condition arises when pores become blocked by oil, bacteria, dead skin cells, and dirt, leading to pimples, commonly referred to as zits or blemishes.
Do you know acne treatment is different from acne scar treatment?
Acne and acne scars are two related but distinct skin concerns. While acne involves the presence of pimples, blackheads, and other blemishes on the skin, acne scars are the marks left behind after acne heals. Understanding the differences between treating acne and treating acne scars is essential for achieving clear, healthy skin.
Types of Acne
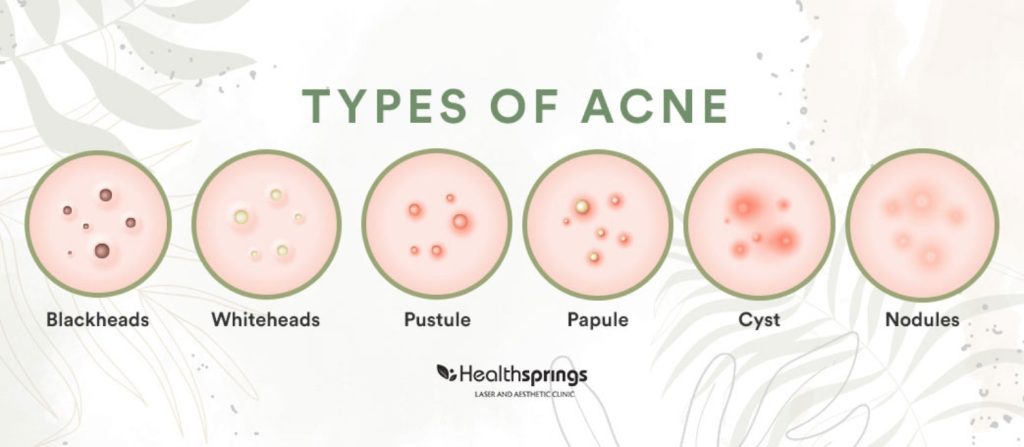
Acne can manifest in various forms, including:
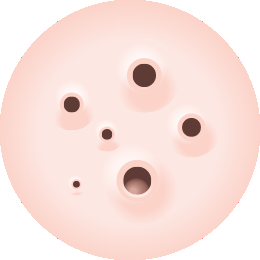
BLACKHEADS AND WHITEHEADS
They are simply clogged pores that are not inflamed. They can be seen blocked below the surface of the skin. Oil, dead skin cells and bacteria accumulate and block pores that result to small bumps in the surface of the face. Easily treatable since they are not inflamed and do not need any serious medication.
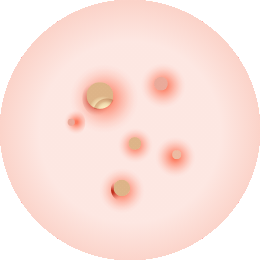
PAPULES
Inflamed acne starts when a clogged pore grows irritated and becomes inflamed. It swells, appears reddish, and is painful.

PUSTULES
They are inflamed lesions that are generally filled with pus. They may appear white or yellow in colour, and popping pustules can lead to acne scarring
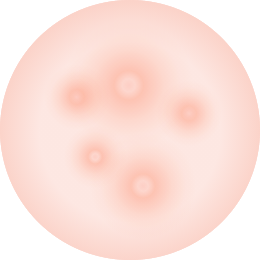
NODULES
Nodules are another type of inflammatory acne lesions that develop under the skin. It can be seen as large, hard, painful bumps that embed under the skin surface during the later stages of acne breakouts. They look like papules but they are larger, raw and painful to touch. They generally do not contain pus. It can last long for weeks or months, difficult to treat, and it causes dark acne scars.

CYSTS
They are a severe form of acne lesion that are inflamed and filled with pus when oil ducts and pores become clogged and rupture. They are generally painful and require professional medical treatment.

MASKNE
Wearing a face mask help prevent the spread of COVID-19 and it has become part of our ‘daily wardrobe’. However, wearing face masks may have side effects on our skin.

BLACKHEADS AND WHITEHEADS
They are simply clogged pores that are not inflamed. They can be seen blocked below the surface of the skin. Oil, dead skin cells and bacteria accumulate and block pores that result to small bumps in the surface of the face. Easily treatable since they are not inflamed and do not need any serious medication.

NODULES
Nodules are another type of inflammatory acne lesions that develop under the skin. It can be seen as large, hard, painful bumps that embed under the skin surface during the later stages of acne breakouts. They look like papules but they are larger, raw and painful to touch. They generally do not contain pus. It can last long for weeks or months, difficult to treat, and it causes dark acne scars.

PAPULES
Inflamed acne starts when a clogged pore grows irritated and becomes inflamed. It swells, appears reddish, and is painful.

PUSTULES
They are inflamed lesions that are generally filled with pus. They may appear white or yellow in colour, and popping pustules can lead to acne scarring

CYSTS
They are a severe form of acne lesion that are inflamed and filled with pus when oil ducts and pores become clogged and rupture. They are generally painful and require professional medical treatment.

MASKNE
Wearing a face mask help prevent the spread of COVID-19 and it has become part of our ‘daily wardrobe’. However, wearing face masks may have side effects on our skin.
Symptoms of Acne
Acne symptoms can include:
- Rough, uneven skin texture
- Discoloration such as hyperpigmentation and redness
- Swelling and inflammation
- Pain and tenderness
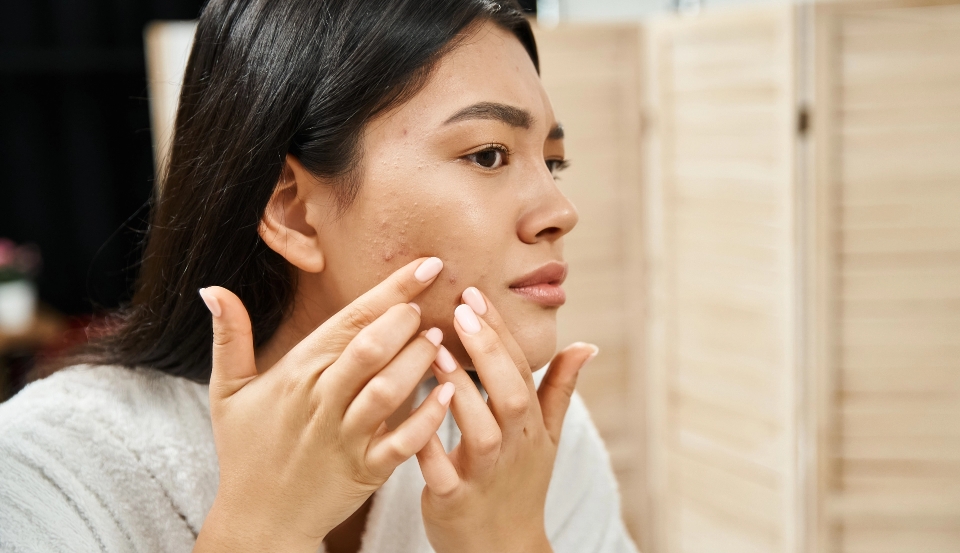


Causes of Acne
Acne is caused by blocked pores due to:
- Excess oil production
- Accumulation of dead skin cells
- Bacterial buildup
Risk Factors for Acne
Acne is caused by blocked pores due to:
- Hormonal changes (e.g., puberty, pregnancy)
- Endocrine conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Cigarette smoking
- Poor sleep and stress
- High oil content in beauty products
- Certain medications
- Family history of acne
- Skin, makeup, and hair products that are comedogenic


Risk Factors for Acne
Acne is caused by blocked pores due to:
- Hormonal changes (e.g., puberty, pregnancy)
- Endocrine conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Cigarette smoking
- Poor sleep and stress
- High oil content in beauty products
- Certain medications
- Family history of acne
- Skin, makeup, and hair products that are comedogenic
Diagnosing Acne
We can diagnose acne by examining the skin and identifying the types and severity of lesions to develop a personalised treatment plan.
Treatment for Acne
Acne treatment varies based on severity:
-
Mild Acne:
Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments like benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid can be effective. -
Moderate Acne:
Prescription-strength medications such as retinoids, antibiotics, and hormonal treatments might be necessary. -
Severe Acne:
Oral antibiotics, topical treatments, and medications like isotretinoin (Accutane) may be recommended. Procedures like Nd:YAG laser, broadband light, chemical peels, and cortisone injections can also help.

Treatment for Acne
Acne treatment varies based on severity:
-
Mild Acne:
Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments like benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid can be effective. -
Moderate Acne:
Prescription-strength medications such as retinoids, antibiotics, and hormonal treatments might be necessary.. -
Severe Acne:
Oral antibiotics, topical treatments, and medications like isotretinoin (Accutane) may be recommended. Procedures like photodynamic therapy (PDT), dermabrasion, chemical peels, and cortisone injections can also help.
Comparison of Acne Treatment |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acne Treatment | Pain Score | Duration | Session Required A Year | ||
| Forever Young BBL | 1 | 🕐🕐 | Monthly | ||
| Chemical Peel | 0 | 🕐🕐 | Monthly | ||
| Cortisone Acne Injection | 1 | 🕐 | When Necessary | ||
| Yellow Laser | 0 | 🕐 | Monthly | ||
| Phototherapy | 1 | 🕐 | Monthly | ||
| Oral Medication | 1 | 🕐 | Daily | ||
| Topical Cream | 0 | 🕐 | Daily | ||
Preventing Acne
Preventative measures include:
- Washing your face daily with an oil-free and pH-balanced cleanser
- Using noncomedogenic (non-pore clogging) skincare products, use a toner to balance your skin’s pH value, apply light-weight moisturiser and avoid using rich face cream.
- Removing makeup before bed
- Reduce dairy and high sugar content food intake
- Maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated
- Reducing stress levels
- Wear oil-free sunblock
- Cover any open wounds or cracks in the skin


Home Remedies for Acne
Some at-home treatments that may help include:
- Applying tea tree oil or aloe vera
- Using a honey mask or green tea refreshers
- Avoiding touching or squeezing pimples to prevent scarring and spread of bacteria
By following a consistent skincare routine and seeking professional advice when needed, managing acne and achieving healthier skin is entirely possible.
Cortisone Injection – a quick, fuss-free solution to get rid of cystic acne!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Acne
Can diet affect acne?
Yes, diet can influence acne. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as sugary snacks and processed foods, may contribute to breakouts. Dairy products have also been linked to acne in some individuals. Maintaining a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage acne.
How often should I wash my face if I have acne?
It’s recommended to wash your face twice daily, once in the morning and once before bed, using a gentle, oil-free cleanser. Over-washing or using harsh scrubs can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
Are there any natural remedies for acne?
Yes, several natural remedies may help manage acne. These include applying tea tree oil, which has antibacterial properties, using aloe vera for its soothing effects, and incorporating honey masks due to honey’s antimicrobial benefits. However, it’s essential to patch-test any natural remedies to ensure they don’t cause irritation.
